Matteo Mazzola – Walking the land of Iside Farm with a regenerative farmer
This is a special episode, the first one ever of the Walking the Land with a Regenerative Farmer, where we walk the land of the farm with a farmer while we talk about regeneration.
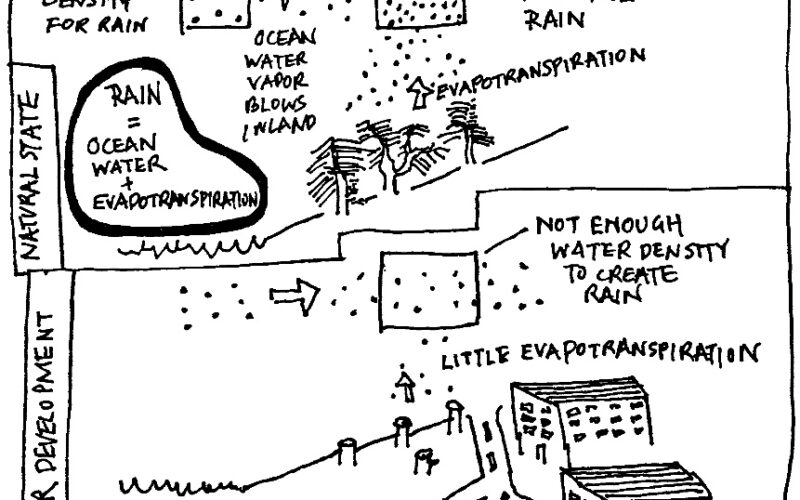
Walking through Iside Farm on the Iseo Lake in Italy, with regenerative farmer Matteo Mazzola, we unlock the secrets of regenerative agriculture as we traverse the innovative landscapes crafted by Matteo, Paola and the Iside crew. We embark on a profound exploration of sustainable farming, showcasing Matteo’s expertise in farm design, water systems, and the integration of olive trees and animals into the land. Learn how access ways are more than just paths across a farm; they’re a vital component in the flow of energy and resources, helping to prevent erosion with concrete strips and alfalfa, and offering additional crop space. Matteo’s wisdom extends to the creative reuse of shipping containers, illustrating a commitment to terraforming that marries functionality with environmental stewardship.